Have you ever wondered about the invisible force that guides compass needles and protects our planet from harmful solar radiation? Look no further than Earth’s magnetic field! But have you ever pondered, “Which layer is responsible for Earth’s magnetic field?” Let’s embark on a journey to uncover this captivating phenomenon.
Which Layer is Responsible for Earth’s Magnetic Field?
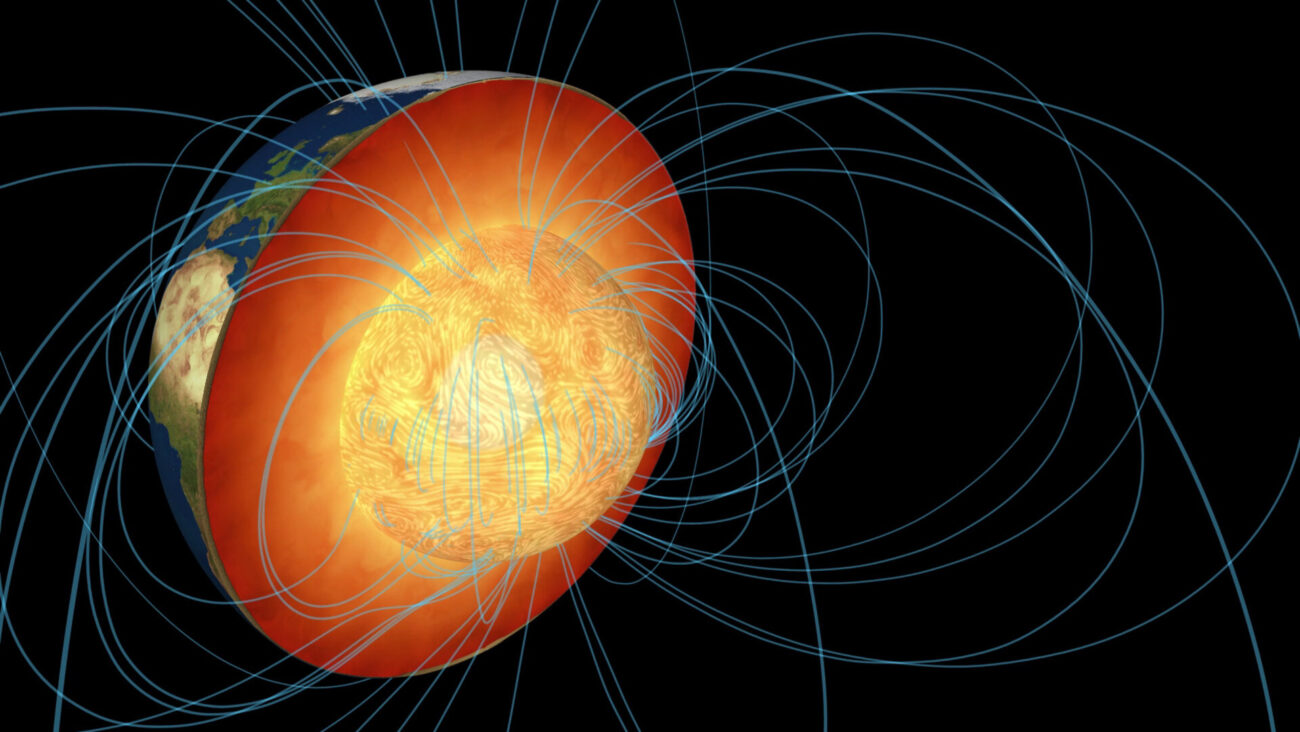
The outer core of the Earth is Responsible for Earth’s Magnetic Field, According to the U.S. Geological Survey. As Earth spins on its own axis, the iron inside the liquid outer core moves around too. This movement causes powerful electric currents to develop in the liquid iron itself. Here the convective energy from the slow-moving molten iron is converted to electrical and magnetic energy.
The outer core of the earth is in a liquid state. The motion of the liquid in the outer core generates electric currents, which in turn generate the Earth’s magnetic field. The outer core is responsible for the earth’s magnetic field.
Understanding Earth’s Magnetic Field
Before delving into the layers responsible for Earth’s magnetic field, let’s understand the basics. Picture Earth as a giant magnet with invisible lines of force encircling it, creating what we call the magnetic field. This field extends from the planet’s interior into space, shielding or protecting us from solar winds and cosmic radiation.
The Inner Dynamo of Earth
Core Dynamics At the heart of Earth’s magnetic prowess lies its core—a scorching-hot, molten metallic sphere comprised mostly of iron and nickel. Deep within this core, swirling currents of molten metal generate electric currents, much like a dynamo, producing the magnetic field. This process, known as the geodynamo, operates in the outer core, where extreme temperatures and pressures facilitate the movement of conductive materials.
The Enigmatic Outer Core of Earth
The outer core, despite being shrouded in mystery due to its inaccessibility, plays a important role in Earth’s magnetic field generation. Its churning, turbulent currents induce electric currents through the process of convection, driving the geodynamo and sustaining the magnetic field. Without the dynamic interplay within the outer core, Earth’s magnetic shield would diminish, leaving us vulnerable to solar storms and cosmic bombardment.
Crust and Mantle
Passive Observers While the crust and mantle layers do not actively generate Earth’s magnetic field, they serve as passive participants, influencing its behavior. The solid crust and semi-solid mantle encapsulate the core, acting as insulating layers that contain and shape the magnetic field’s trajectory. Additionally, movements within the lithosphere, such as plate tectonics and volcanic activity, can modulate the field’s intensity and direction over geological time scales.
The Vanishing Mystery Unraveled
Which layer is responsible for Earth’s magnetic field?
So, to answer the burning question, “Which layer is responsible for Earth’s magnetic field?”—it’s the dynamic interplay within the outer core that holds the key. Through the mesmerizing dance of molten metals and convective currents, Earth’s geodynamo creates and sustains the magnetic shield that envelops our planet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Earth’s magnetic field, a marvel of nature, is a testament to the intricate dynamics at play within our planet’s core. While the core orchestrates this cosmic symphony, the crust and mantle provide a supportive backdrop, shaping and preserving this vital shield. So, the next time you marvel at a compass needle pointing north or witness the aurora dancing across the sky, remember the awe-inspiring forces at work deep beneath our feet.
Hope you liked this information, For more details about Earth’s magnetic field click on this link.
Also Read This –
For all such news from the world, stay connect with us on latestbite.com. Thanks.